


We recognize that the safety and environmental impact issues associated with the disposal of used ternary lithium-ion batteries are serious issues on a global scale. We have been conducting research and development into the disposal of these batteries, which are extremely dangerous carrying the risk of environmental pollution. E-cubed Goals has successfully completed basic experiments to safely and appropriately process and dispose them.
Based on these results, we have filed a patent application. In the future, we will put these results to practical use. We have begun developing specific processing equipment, and are working to help the realization of a sustainable society.

This system utilizes thin-film solar panels, which are installed on the roof (body) of the transport truck or bus, and directly charge the lead battery that is always installed on board. By stabilizing the battery voltage, the alternator (generator), which normally runs automatically while driving is reduced in operation, which in turn reduces the load on the engine and makes it possible to significantly reduce fuel consumption.
In the proof of concept (PoC), a reduction of more than 10% in fuel consumption has been
confirmed, which will make a significant contribution to reducing CO2 emissions in the transport
industry. In addition, the CO2 emission credits created by the introduction of this technology can
be bought and sold on the carbon market, creating a new economy. By improving efficiency in
both fuel consumption and CO2 emissions reduction in the transportation industry, we will realize
a step towards a sustainable future.
*1 "GasHeru" is a registered trademark of Oshu Bussan Unyu Co., Ltd.
This system was developed in collaboration with Oshu Bussan Unyu Co., Ltd.
*2 Our company holds exclusive sales rights for this solution overseas, excluding Japan.
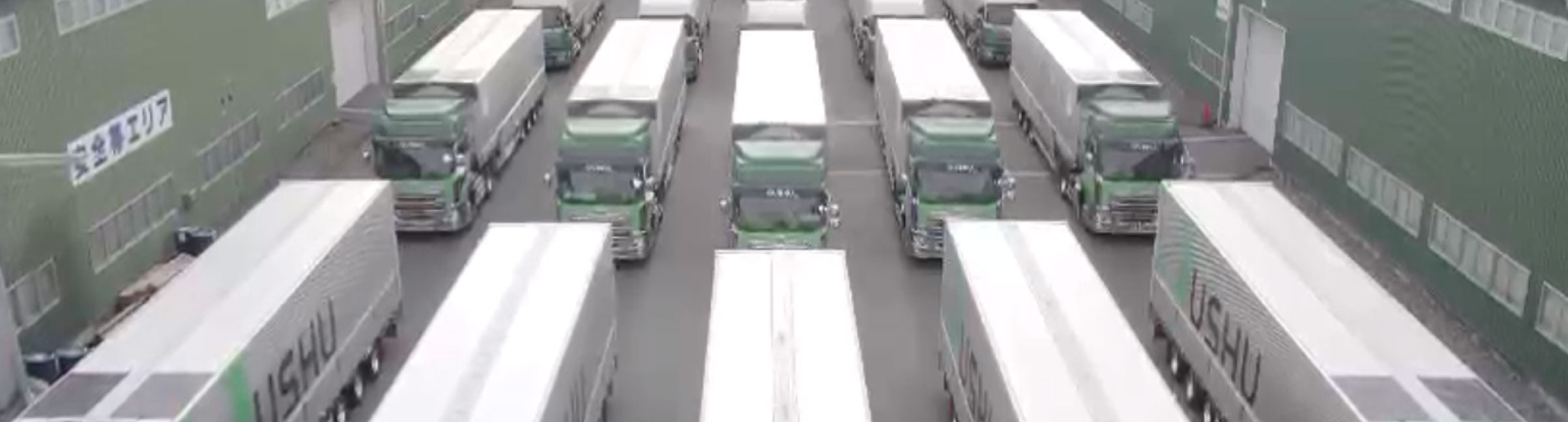

※Thin-film solar panels (installed on all trucks)

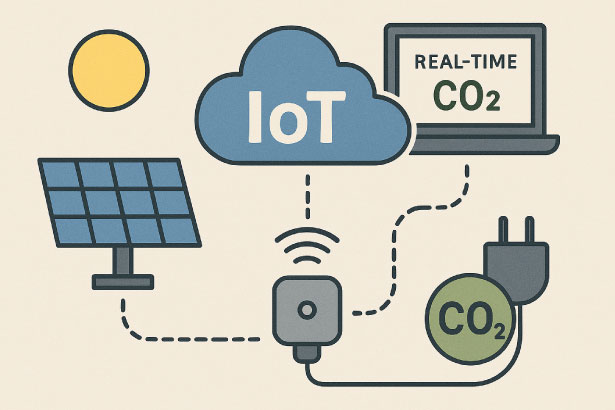
The IoT device functions as an important infrastructure that collects and records the status of renewable energy usage and the amount of CO2 emission rights generated in real time. IoT sensors are installed on solar power generation facilities and power-using equipment constantly monitors the amount of power generated, power consumed, CO2 conversion data, and automatically collects the essential information for the accurate calculation of emission rights. The IoT device makes it possible to "visualize" the environmental contribution, which was previously ambiguous, and by linking it with blockchain, fraud-free data management and emission rights trading will become possible.
Furthermore, IoT will not only collect information, but will also network the "sources" of CO2
emission rights for each region and facility. And in the future, the device will play a central role in
a "distributed emission rights platform" that will link across countries and industries. We will
utilize the transparency and immediacy of IoT to provide a highly reliable digital infrastructure in
the emission rights market. This is being carried out with Waseda University, our joint research
partner.

The Carbon Credit Certification System is a mechanism that makes the effects of activities to reduce and absorb greenhouse gases, including CO2, visible, and allows them to be certified and traded in an internationally trusted manner. This system uses technologies such as IoT and blockchain to accurately measure and record in real time the reduction amounts resulting from various projects, such as the introduction of renewable energy,
forest conservation, and the
introduction of energy-saving technologies. This ensures transparency of reduction effects and
enables fair credit issuance without fraud. Certified credits can be used for carbon offsets and
decarbonization strategies throughout the supply chain, and can demonstrate concrete
contributions to creating a sustainable society in numerical terms.

